|
|
- Intelligent Indoor Spatial Sensing
- Artificial Intelligence Security
- 2D/3D Shape and Image Processing
- Visual-based
- Geomagnetic-based
- Wi-Fi Fingerprint-based
- Multi-modal Fusion-based
- Fingerprint Database
Introduction
Visual Indoor Localization
|
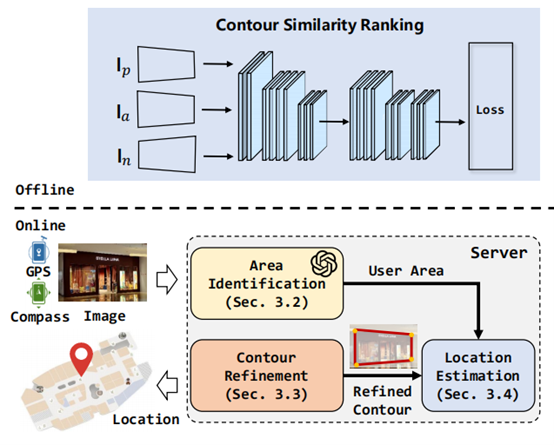
LLM‐Loc: Bootstrap Single-Image Indoor Localization with Large Language Model
Qun Niu, Tao Chen, Xing Zhang, Yifan Wang, Ning Liu*
|
|
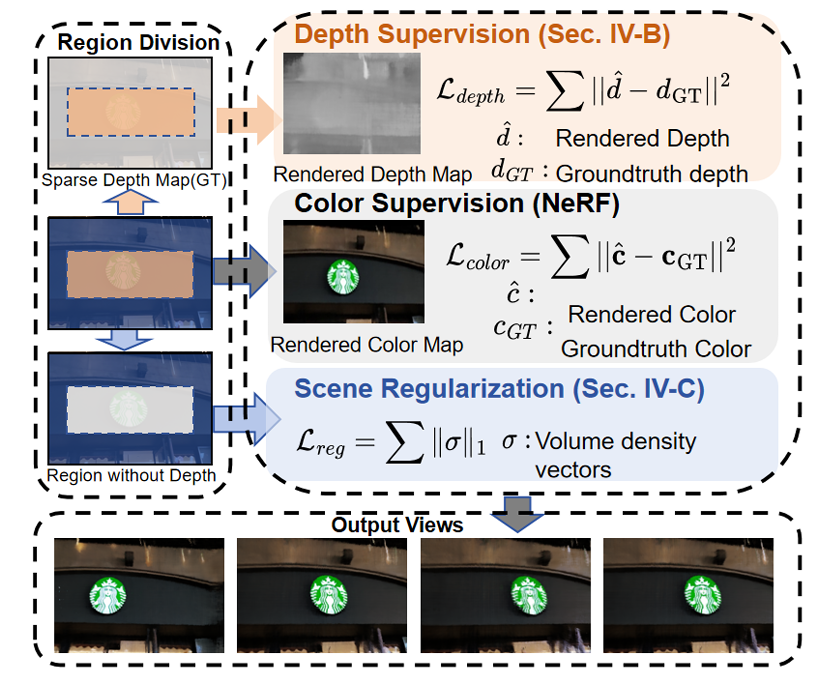
NeRF‐VLD: Efficient Visual Landmark Database Construction via Scene Constraints
Tao Chen, Qun Niu*, Ning Liu
|

|
Resource efficient and Automated Image-based Indoor Localization
Qun Niu, Mingkuan Li, Suining He, Chengying Gao*, S.-H. Gary Chan and Xiaonan Luo
|

|
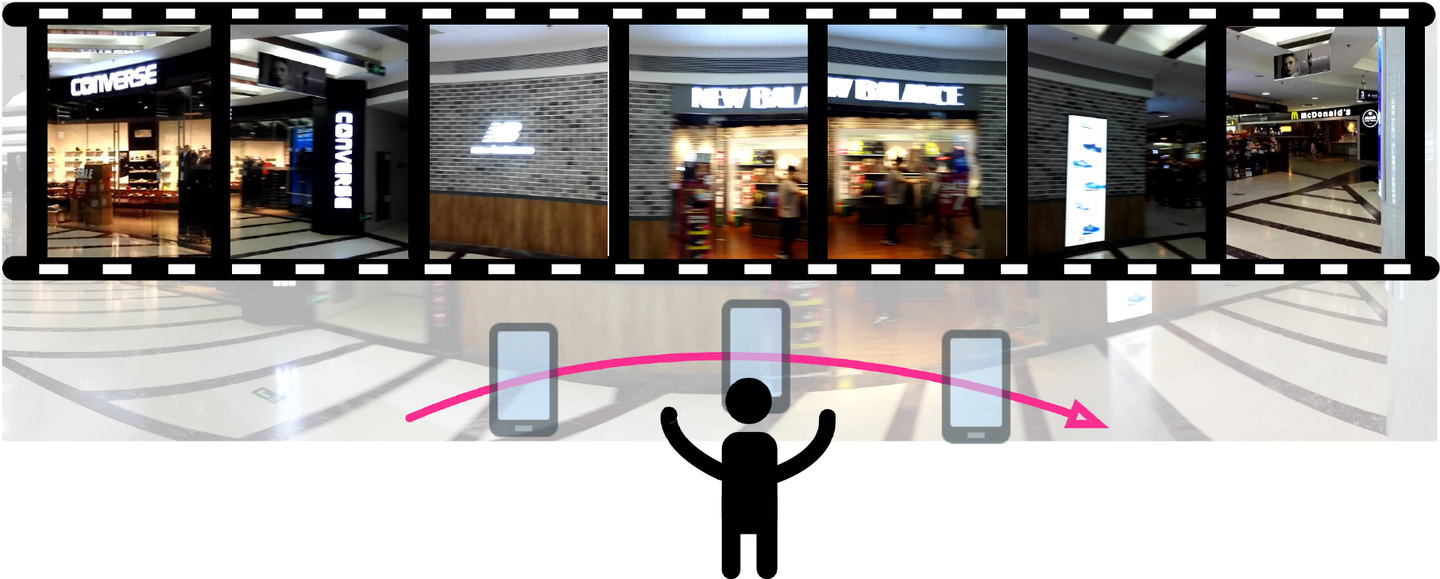
SweepLoc: Automatic Video-based Indoor Localization by Camera Sweeping
Mingkuan Li, Ning Liu*, Qun Niu, Chang Liu, S.-H. Gary Chan, Chengying Gao
|
Geomagnetic Indoor Localization
|
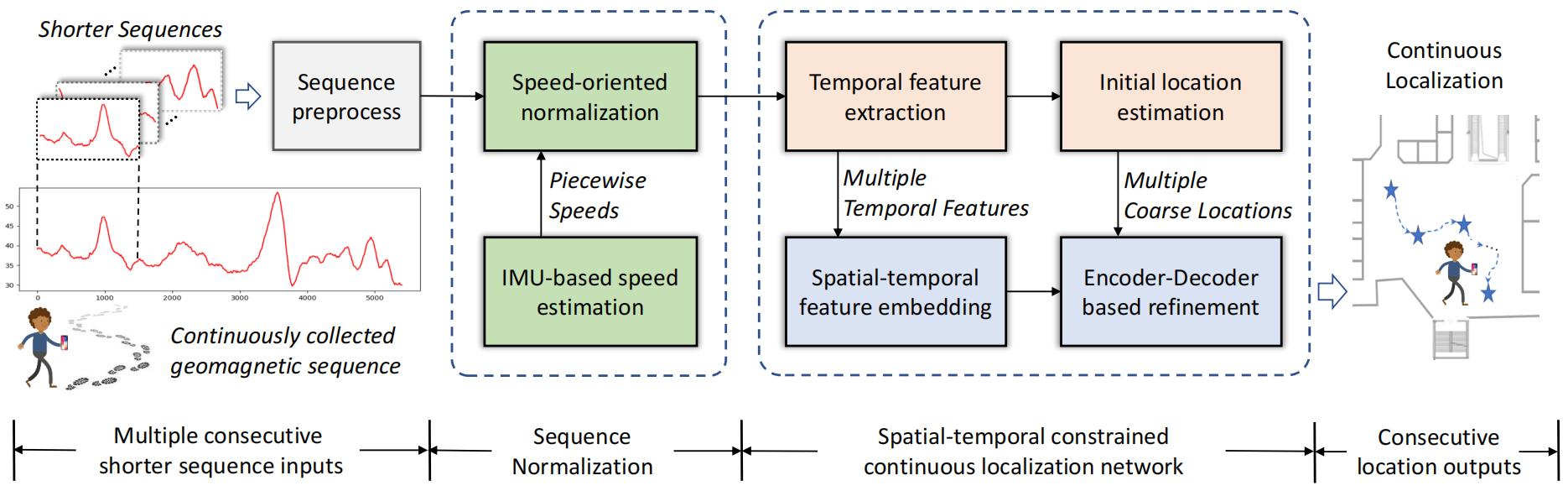
Spatio-temporal Constrained Geomagnetic Indoor Localization with Arbitrary Walking Speed
Ning Liu, Gezhi Peng, Hua-Bao Ling, Qun Niu, and Tao He*
|
|
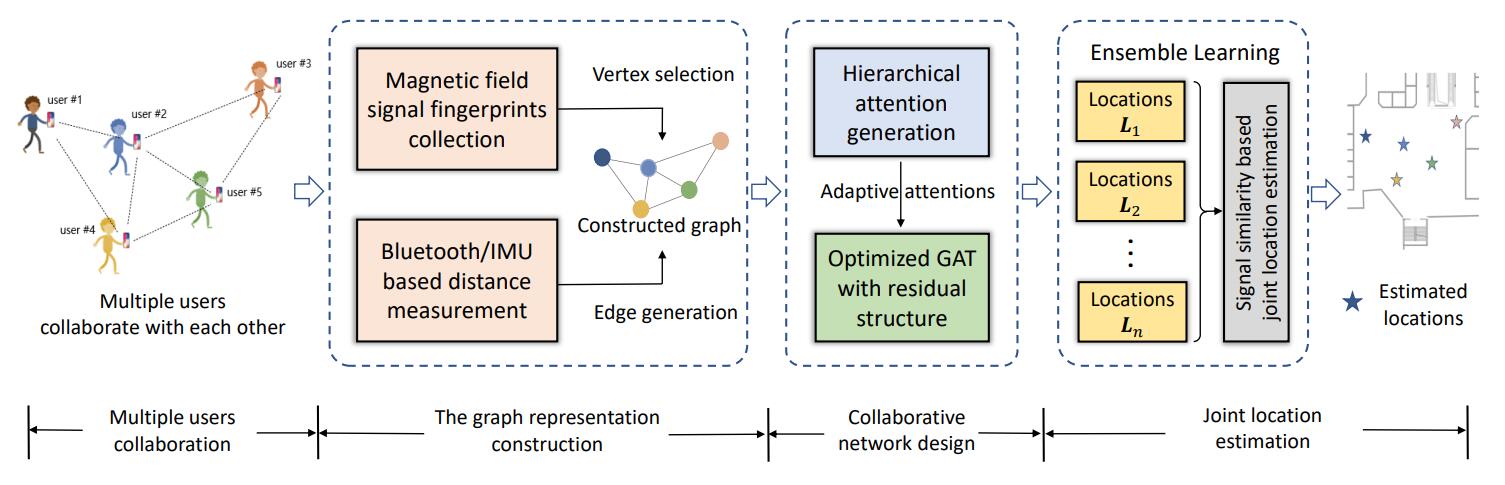
GC-Loc: A Graph Attention Based Framework for Collaborative Indoor Localization Using Infrastructure-free Signals
Tao He, Qun Niu and Ning Liu
|
|
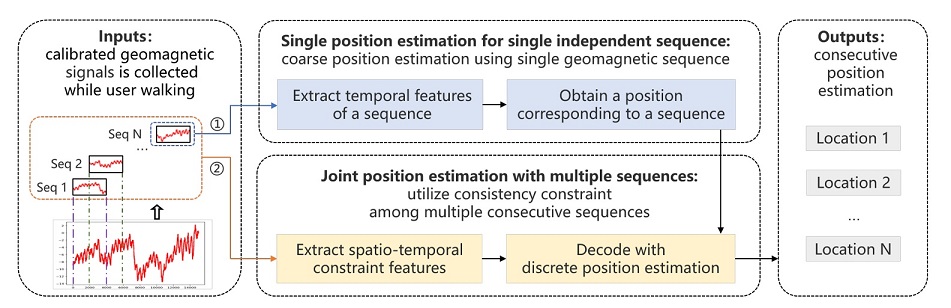
Efficient Indoor Localization with Multiple Consecutive Geomagnetic Sequences
Hui Zhuang, Tao He, Qun Niu and Ning Liu*
|
|
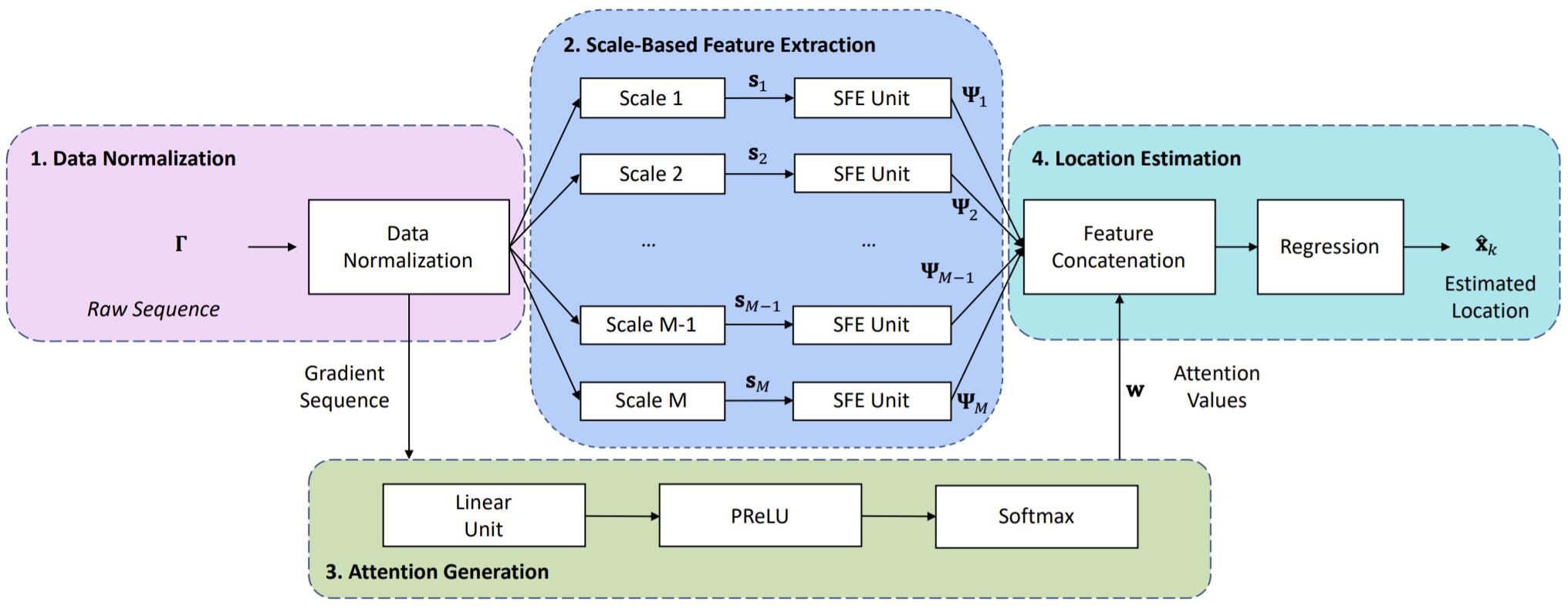
MAIL: Multi-Scale Attention-Guided Indoor Localization Using Geomagnetic Sequences
Qun Niu, Tao He, Ning Liu, Suining He, Xiaonan Luo, Fan Zhou
|
|
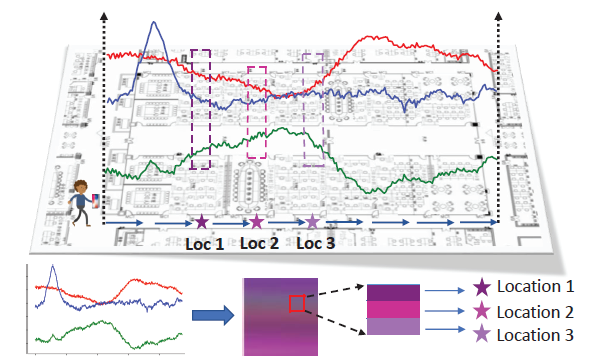
Indoor Localization with Spatial and Temporal Representations of Signal Sequences
Tao He, Qun Niu, Suining He and Ning Liu
|
Wi-Fi Fingerprint-based Indoor Localization
|
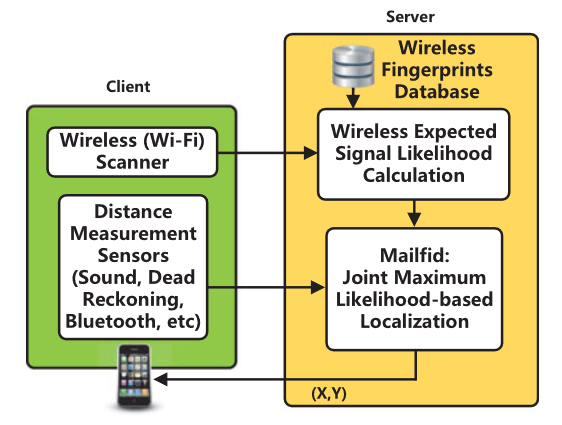
Maxlifd: Joint Maximum Likelihood Localization Fusing Fingerprints and Mutual Distances
Suining He, S.-H. Gary Chan, Lei Yu and Ning Liu*
|
|
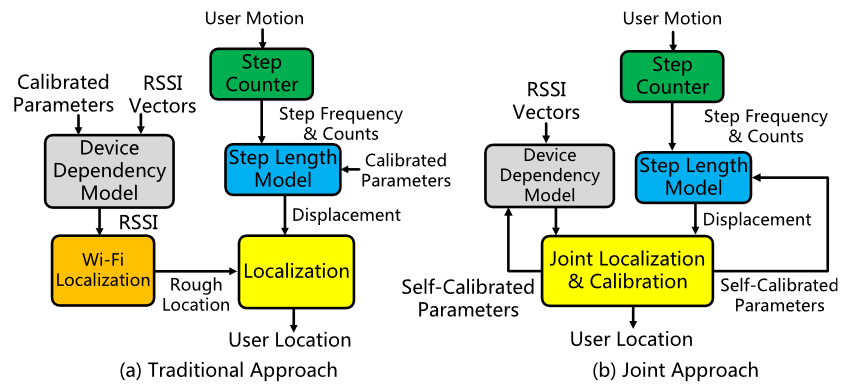
SLAC: Calibration-Free Pedometer-Fingerprint Fusion for Indoor Localization
Suining He, S.-H. Gary Chan, Lei Yu and Ning Liu*
|
Multi-modal Fusion-based Indoor Localization
|
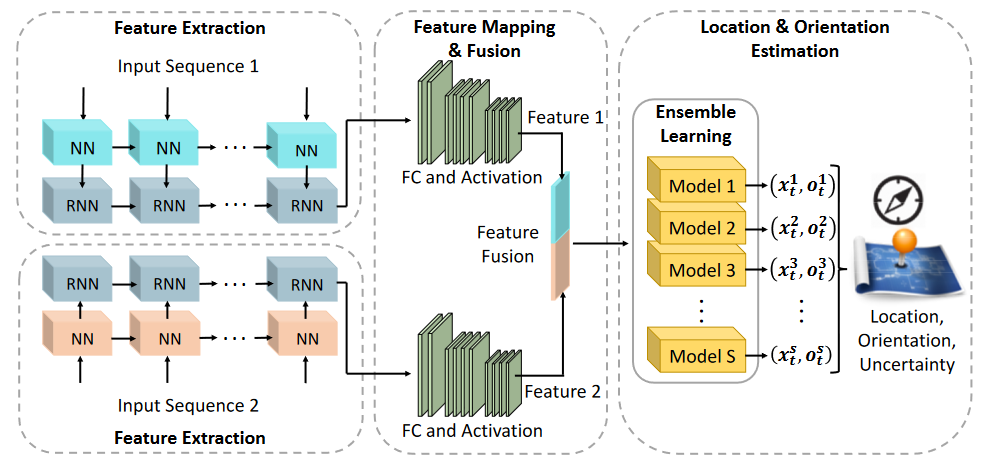
DeepNavi: A Deep Signal-Fusion Framework for Accurate and Applicable Indoor Navigation
Qun Niu, Ning Liu*, Jianjun Huang, Yangze Luo, Suining He, Tao He, S.-H. Chan and Xiaonan Luo
|
Incrementive Reconstruction of Fingerprint Database
|
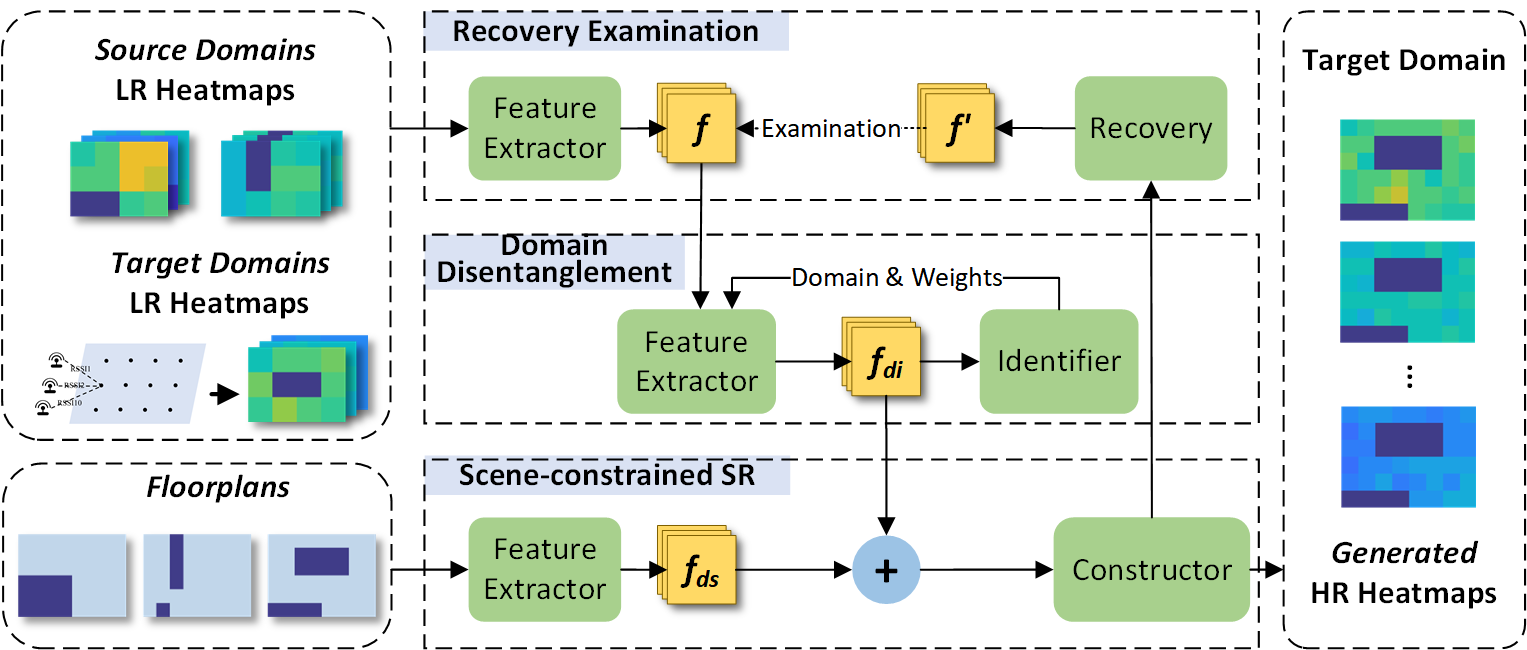
Fast Radio Map Construction with Domain Disentangled Learning for Wireless Localization
Weina Jiang, Lin Shi, Qun Niu and Ning Liu*
|
|
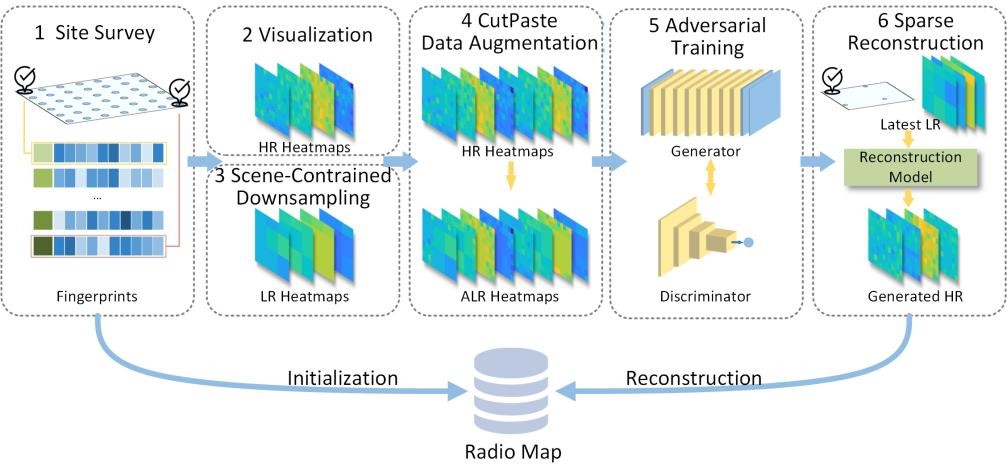
Adaptive Radio Map Reconstruction via Adversarial Wireless Fingerprint Learning
Weina Jiang, Qun Niu, Suining He and Ning Liu*
|
|
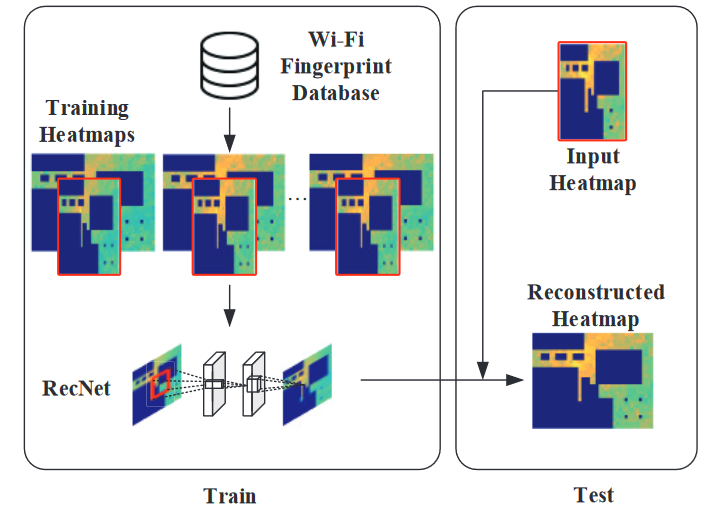
RecNet: A Convolutional Network for Efficient Radiomap Reconstruction
Q. Niu, Y. Nie, S. He, N. Liu and X. Luo
|
