|
|
- Intelligent Indoor Spatial Sensing
- Artificial Intelligence Security
- 2D/3D Shape and Image Processing
- Sketch Generation and Applications
- Image Editing and Synthesis
- 3D Pose Estimation and Motion Generation
- Garment Modeling and Virtual Try-on
- Multimedia Processing & 3D Rendering and Modeling
Sketch Generation and Applications
|

|
|
|

|
Joint Stroke Tracing and Correspondence for 2D Animation
Haoran Mo, Chengying Gao* and Ruomei Wang
|

|
Text-based Vector Sketch Editing with Image Editing Diffusion Prior
Haoran Mo, Xusheng Lin, Chengying Gao* and Ruomei Wang
|
|
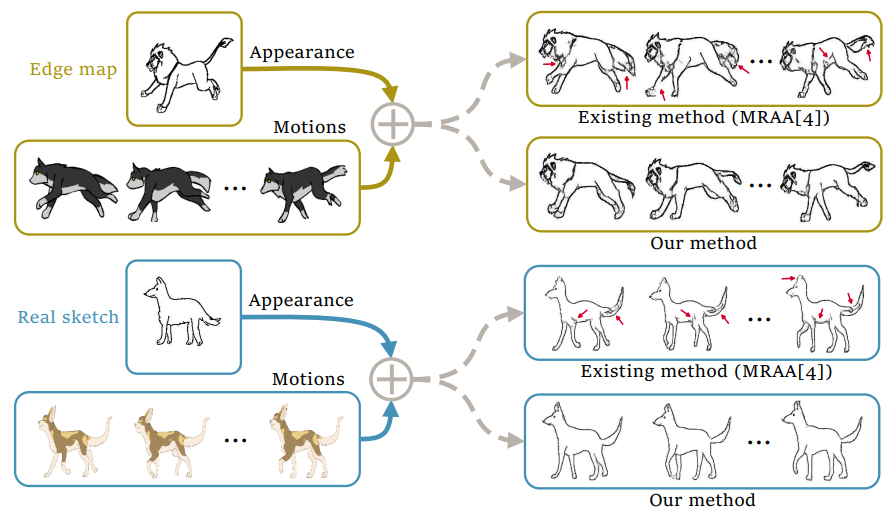
Video-Driven Sketch Animation via Cyclic Reconstruction Mechanism
Zhuo Xie, Haoran Mo and Chengying Gao*
|
|
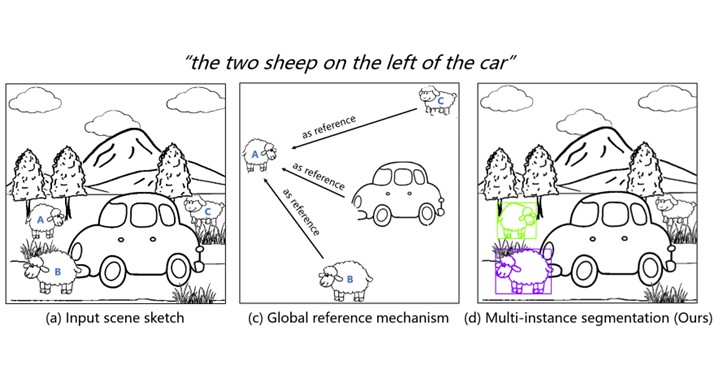
Multi-instance Referring Image Segmentation of Scene Sketches based on Global Reference Mechanism
Peng Ling, Haoran Mo and Chengying Gao*
|
|
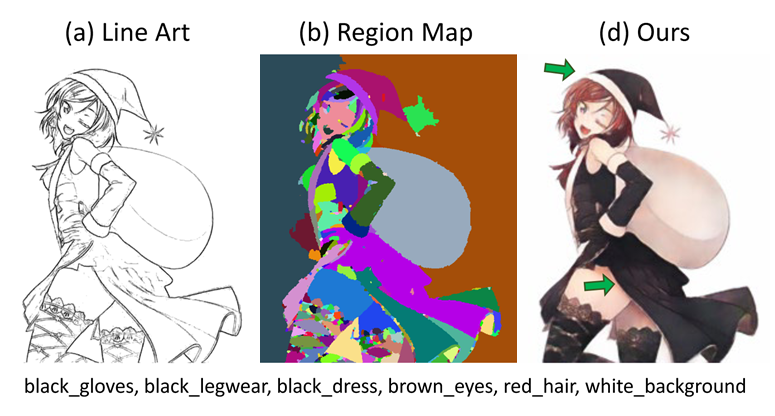
Line Art Colorization Based on Explicit Region Segmentation
Ruizhi Cao, Haoran Mo and Chengying Gao*
|
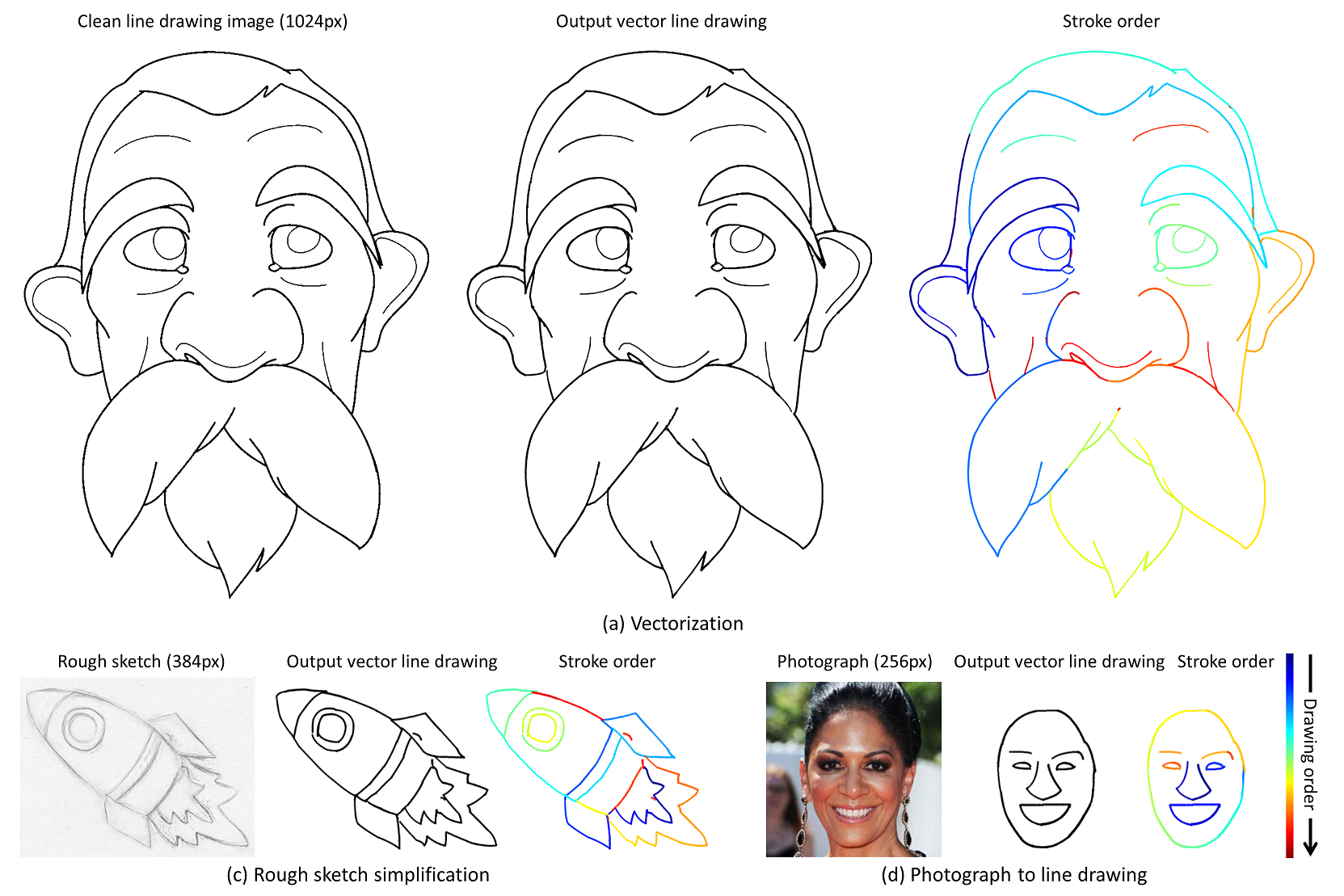
|
General Virtual Sketching Framework for Vector Line Art
Haoran Mo, Edgar Simo-Serra, Chengying Gao*, Changqing Zou and Ruomei Wang
|

|
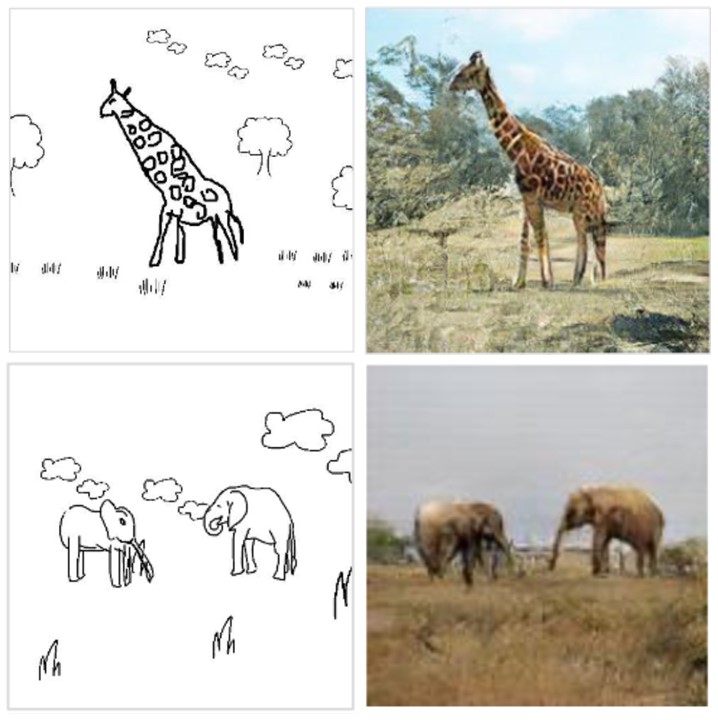
SketchyCOCO: Image Generation from Freehand Scene Sketches
Chengying Gao, Qi Liu, Qi Xu, Jianzhuang Liu, Limin Wang, Changqing Zou*
|
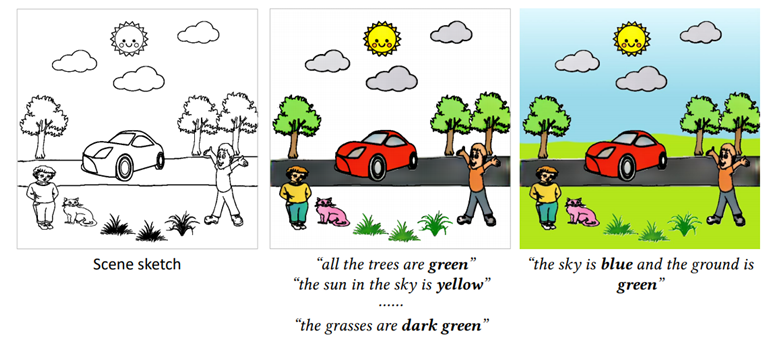
|
Language-based Colorization of Scene Sketches
Changqing Zou#, Haoran Mo#(joint first author), Chengying Gao*, Ruofei Du and Hongbo Fu
|

|
SketchyScene: Richly-Annotated Scene Sketches
Changqing Zou#, Qian Yu#, Ruofei Du, Haoran Mo, Yi-Zhe Song, Tao Xiang, Chengying Gao, Baoquan Chen*, and Hao Zhang
|
Image Editing and Synthesis
Including: image inpainting, color restoration, color transfer and non-photorealistic rendering.

|
Controllable Anime Image Editing via Probability of Attribute Tags
Zhenghao Song, Haoran Mo, and Chengying Gao*
|

|
CAP-VSTNet: Content Affinity Preserved Versatile Style Transfer
Linfeng Wen, Chengying Gao*, Changqing Zou
|
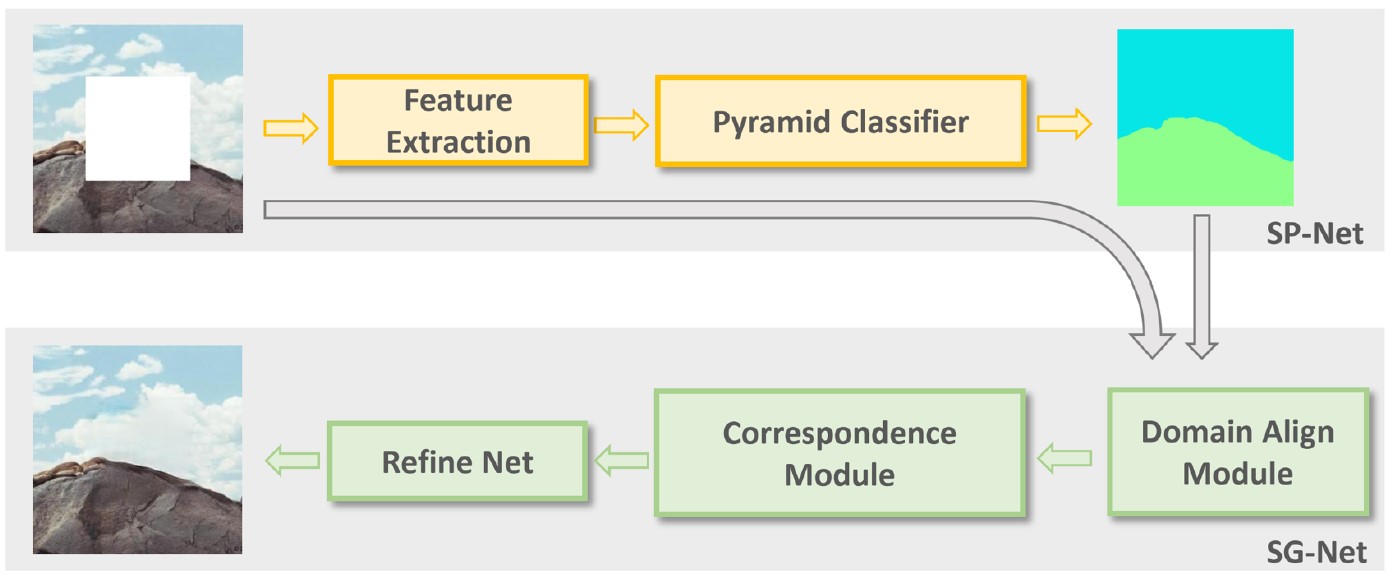
|
Structural Prior Guided Image Inpainting for Complex Scene
Shuxin Wei, Chengying Gao
|
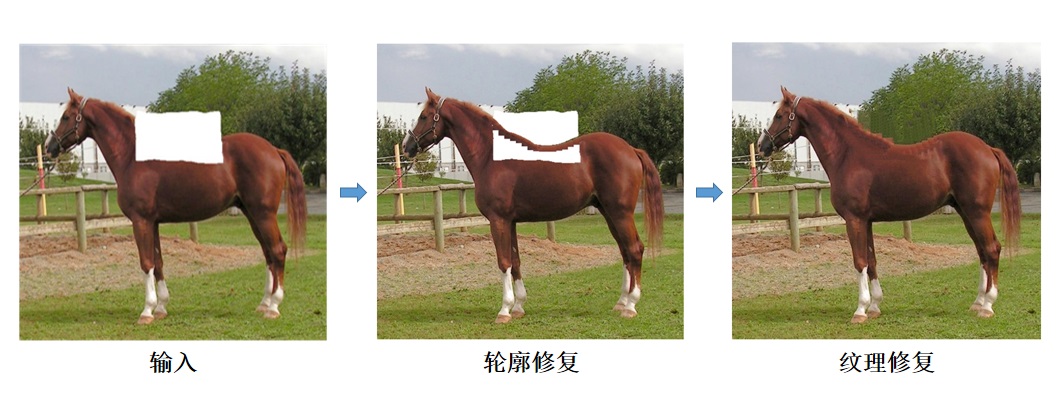
|
基于稀疏结构的复杂物体修复
高成英,徐仙儿,罗燕媚,王栋
|

|
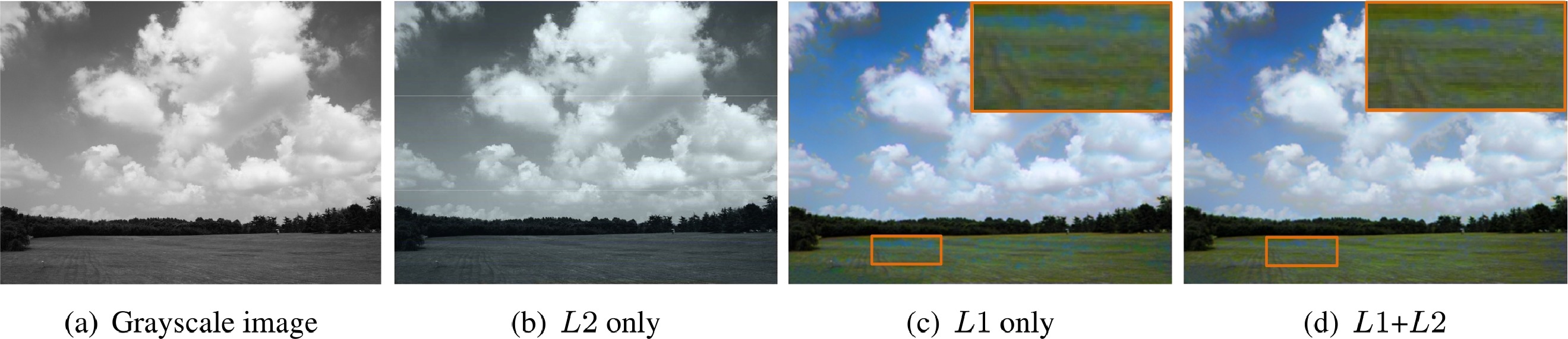
An edge-refined vectorized deep colorization model for grayscale-to-color images
Zhuo Su, Xiangguo Liang, Jiaming Guo, Chengying Gao, Xiaonan Luo
|

|
PencilArt: A Chromatic Penciling Style Generation Framework
Chengying Gao, Mengyue Tang, Xiangguo Liang, Zhou Su, Changqing Zou
|
3D Pose Estimation and Motion Generation
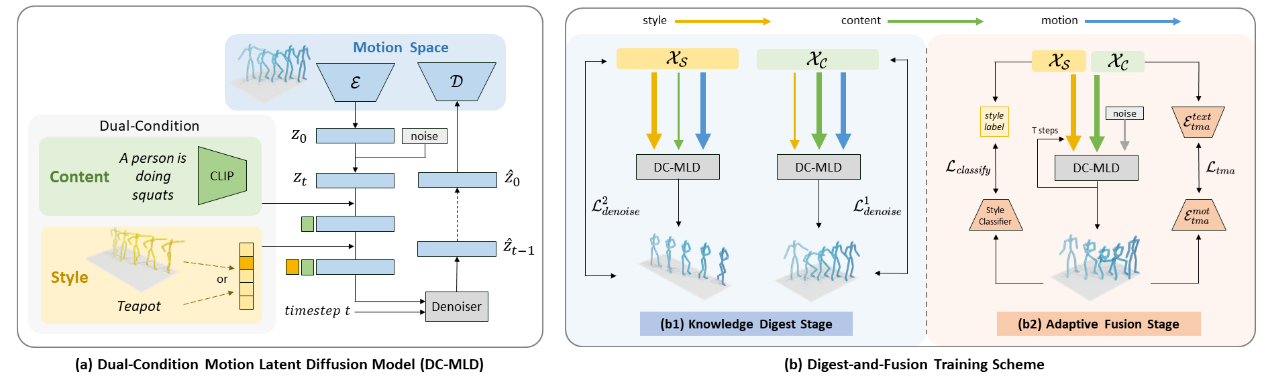
|
DiFusion: Flexible Stylized Motion Generation Using Digest-and-Fusion Scheme Yatian Wang, Haoran Mo, Chengying Gao*
|
|
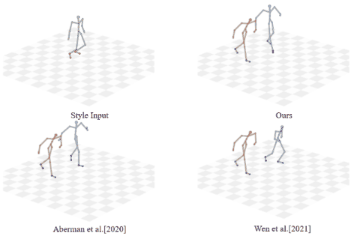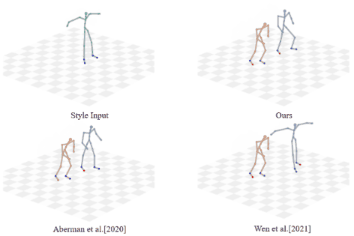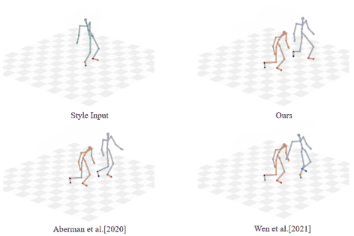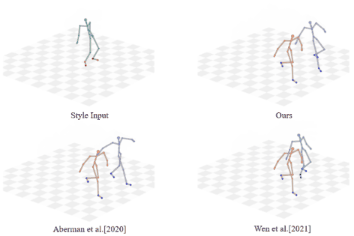
Unpaired Motion Style Transfer with Motion-oriented Projection Flow Network
Yue Huang, Haoran Mo, Xiao Liang, Chengying Gao*
|
|
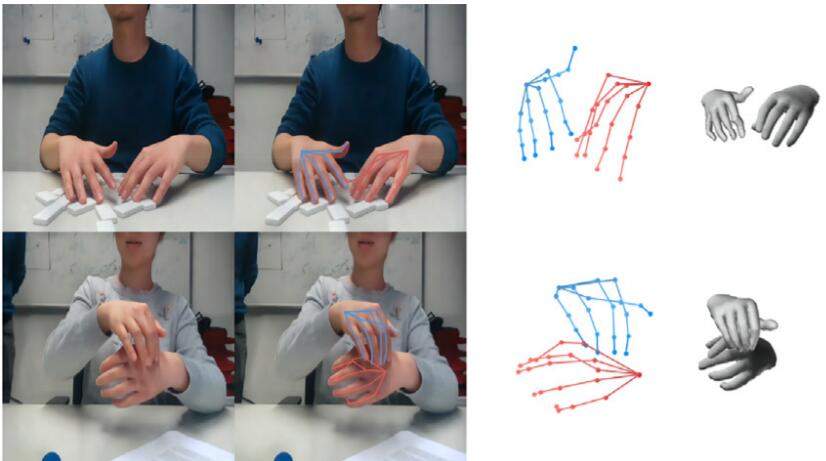
3D interacting hand pose and shape estimation from a single RGB image
Chengying Gao*, Yujia Yang, Wensheng Li
|
Garment Modeling and Virtual Try-on

|
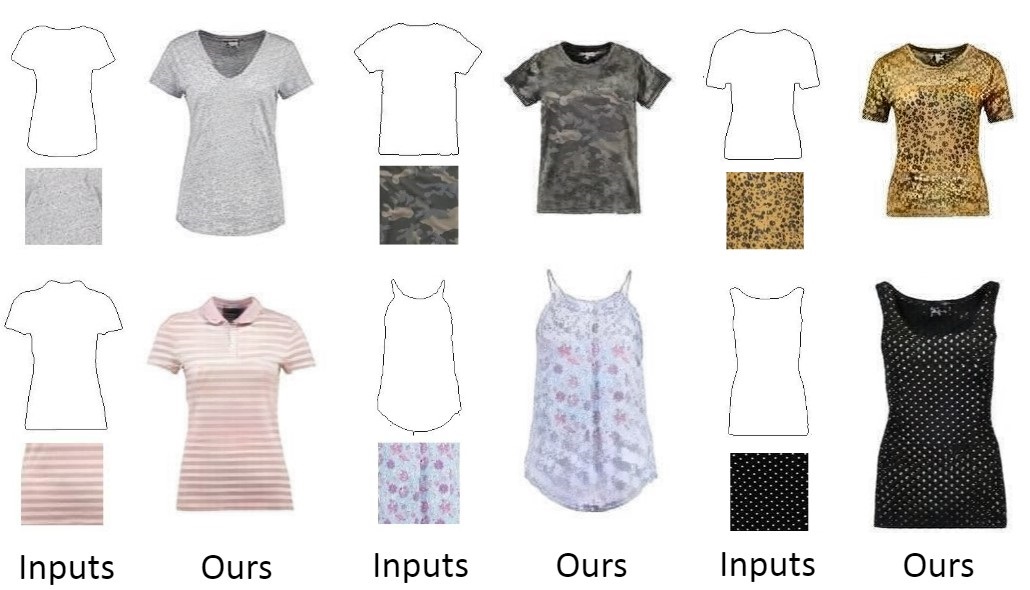
Controllable Garment Image Synthesis Integrated with Frequency Domain Features Xinru Liang, Haoran Mo, Chengying Gao*
|

|
FashionGAN: Display your fashion design using Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets Yirui Cui, Qi Liu, Chengying Gao*, Zhuo Su
|
|
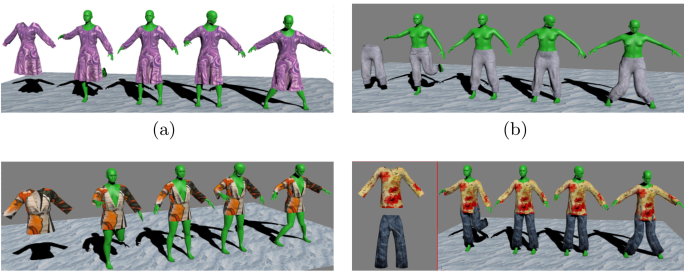
Automatic 3D Garment Fitting Based on Skeleton Driving Haozhong Cai, Guangyuan Shi, Chengying Gao*, Dong Wang
|
Multimedia Processing & 3D Rendering and Modeling
Multimedia Processing: generation and understanding of music and dance.
3D Rendering and Modeling: dynamic human reconstruction and nrural rendering,
fast fluid surface reconstruction based on narrow band method and fabric modeling and rendering.
|
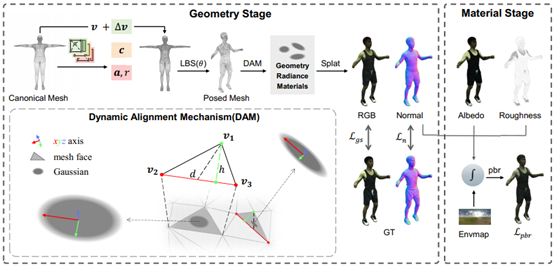
ReGA: Relighting Dynamic Gaussian Avatars from Sparse Views
Lingzhe Zeng, Wensheng Li, Rongbin Zheng, Chengying Gao*
|
|
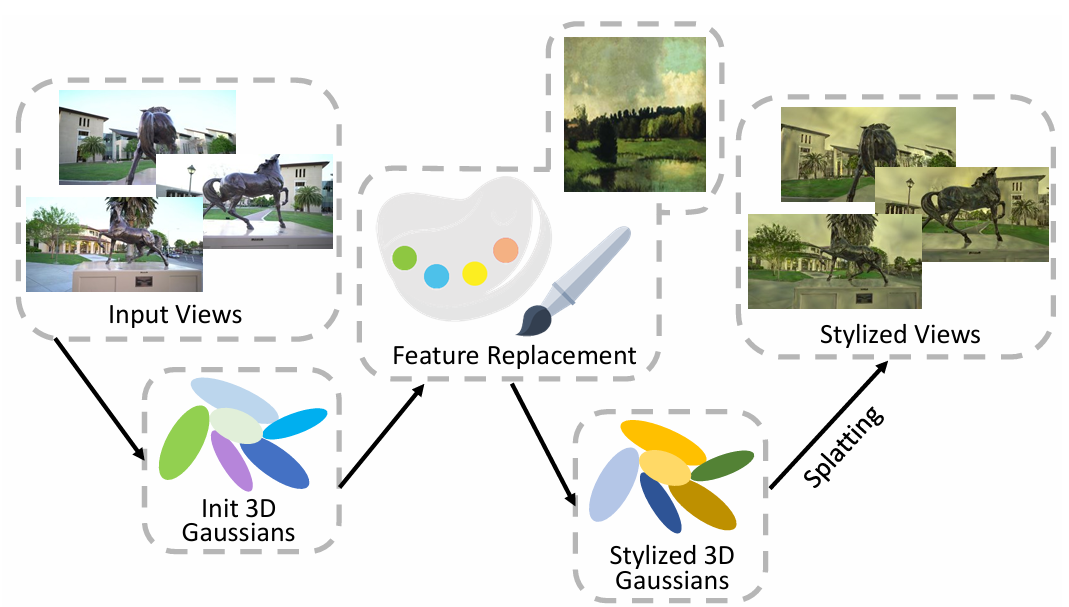
Feature Replacement in Gaussian Splatting for 3D Stylization
Jinkeng Zhu, Wensheng Li, ChengYing Gao*
|

|
Efficient Integration of Neural Representations for Dynamic Humans
Wensheng Li, Lingzhe Zeng, Chengying Gao, Ning Liu*
|

|
DanceComposer: Dance-to-Music Generation Using a Progressive Conditional Music Generator
Xiao Liang, Wensheng Li, Lifeng Huang and Chengying Gao
|
|
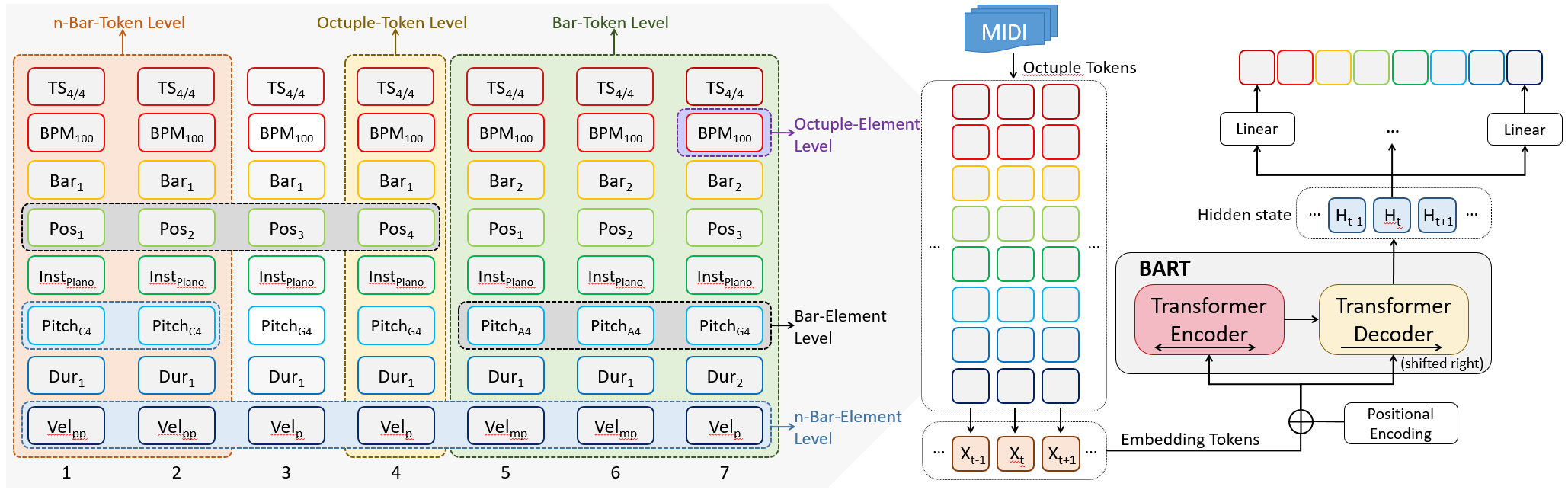
PianoBART: Symbolic Piano Music Generation and Understanding with Large-Scale Pre-Training
Xiao Liang, Zijian Zhao, Weichao Zeng, Yutong He, Fupeng He, Yiyi Wang and Chengying Gao
|
|
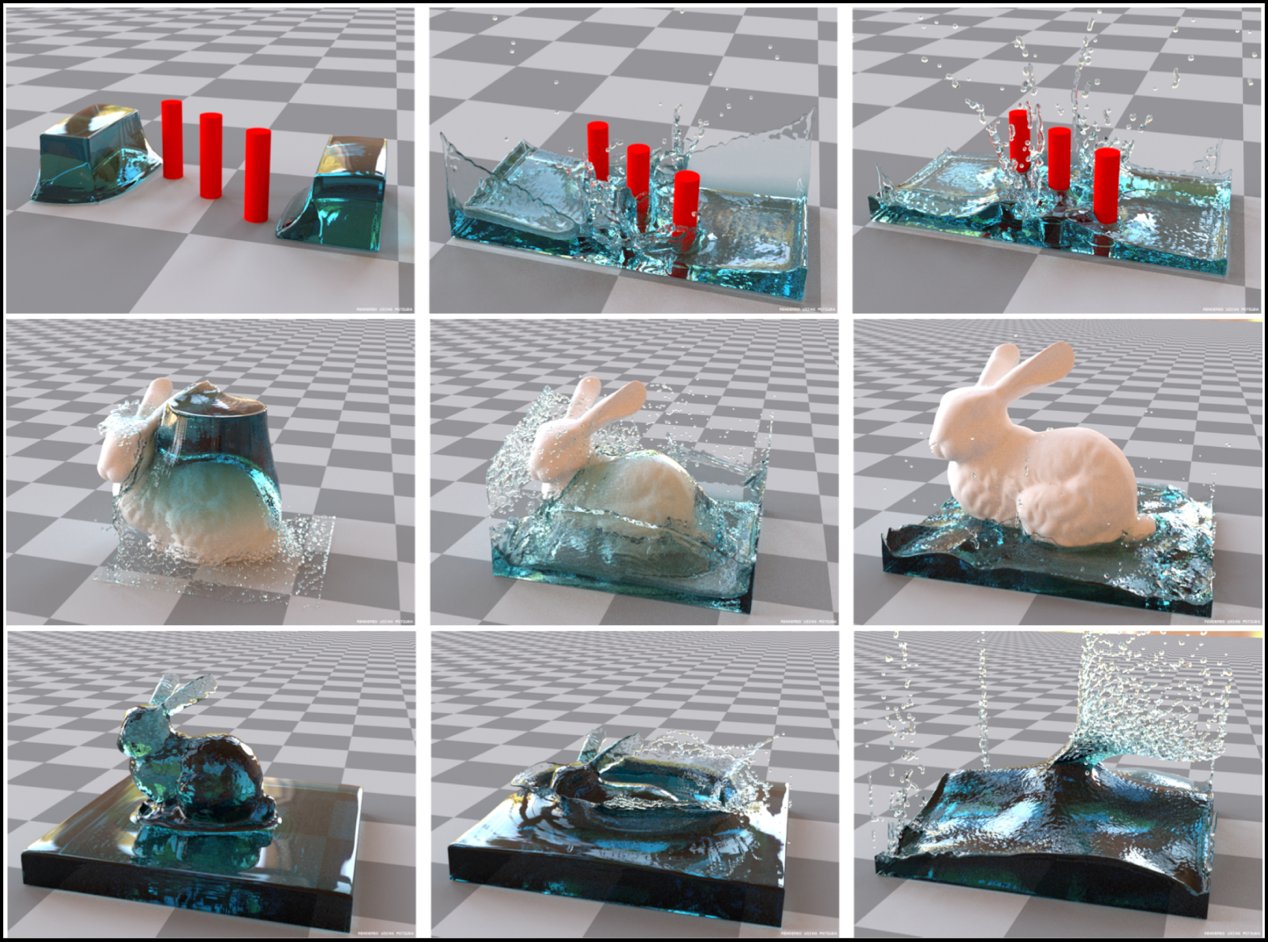
A Completely Parallel Surface Reconstruction Method for Particle-Based Fluids
Wencong Yang, Chengying Gao
|
|
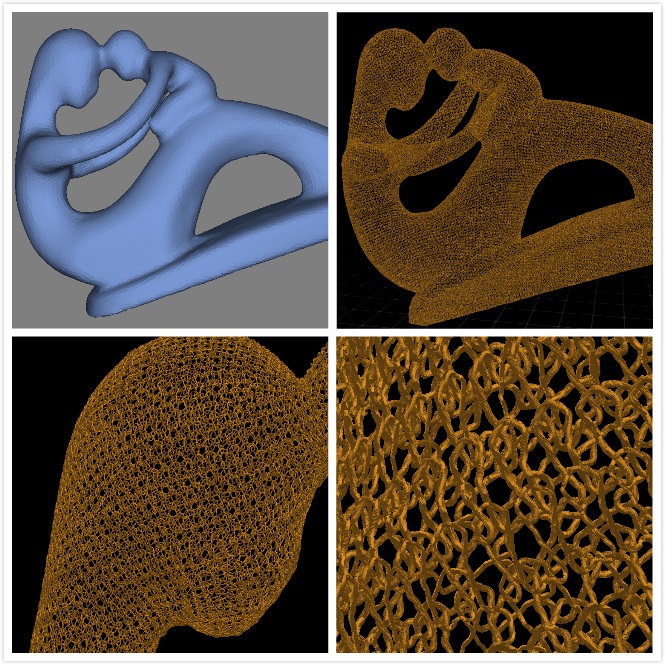
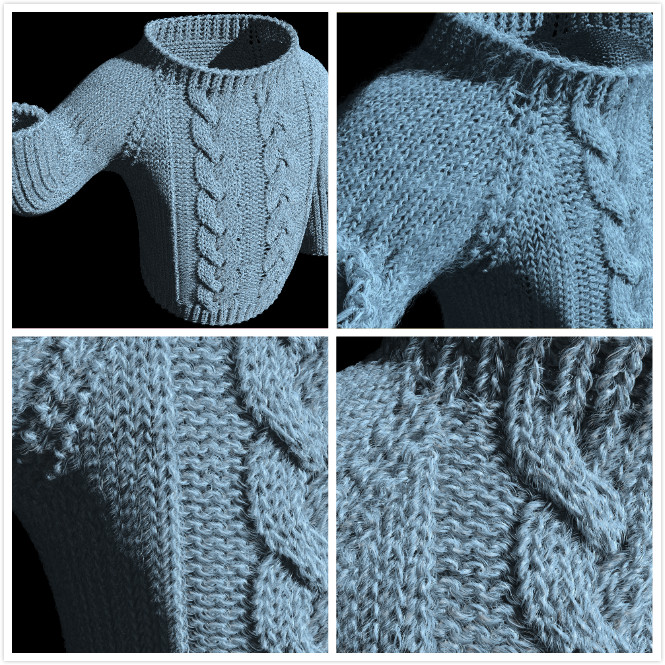
Fully automatic algorithm on yarn model generation
Zekun Zhang
|

|
Microscopic model based real time algorithm on fabric rendering
Xingrong Luo
|
